2024 Confirmed as Warmest Year on Record Globally
The Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) has officially confirmed that 2024 was the warmest year on record globally, marking the first calendar year in which the average global temperature exceeded 1.5°C above its pre-industrial level. This milestone highlights the ongoing impact of human-induced climate change as the primary driver of extreme air and sea surface temperatures.
Collaborative Efforts in Climate Monitoring
Various organizations involved in global climate monitoring, including ECMWF, NASA, NOAA, the UK Met Office, Berkeley Earth, and the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO), collaborated to release data showcasing the exceptional conditions experienced in 2024. Carlo Buontempo, Director of the Copernicus Climate Change Service, emphasized the importance of evidence-based responses to the climate challenge and the need for swift and decisive action to alter the trajectory of future climate.
Record-Breaking Trends
2024 marked a continuation of record-breaking trends, with each of the past 10 years (2015–2024) ranking among the 10 warmest years on record. The monthly global average temperature exceeded 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels for 11 months of the year, setting a new daily global average temperature record on 22 July 2024 at 17.16°C.
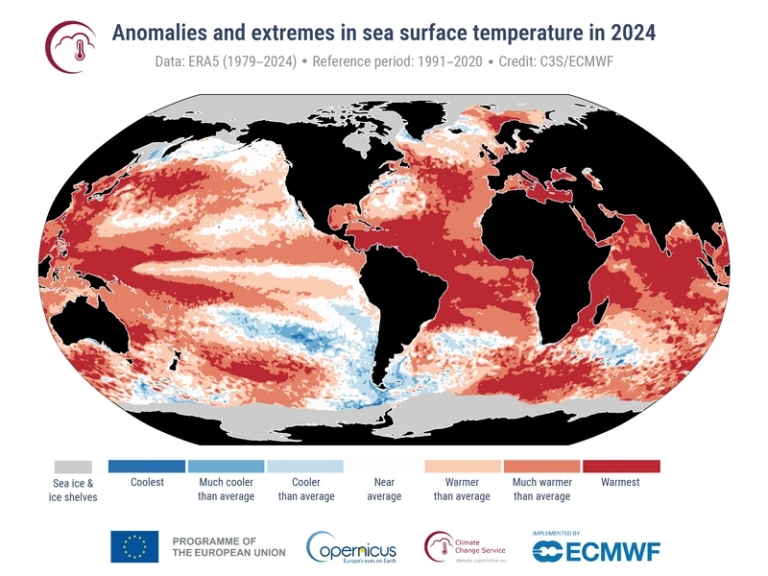
Regional and Oceanic Impacts
2024 was the warmest year for all continental regions, except Antarctica and Australasia, with significant parts of the ocean, particularly the North Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and the western Pacific Ocean, experiencing record warmth. The annual average sea surface temperature over the extra-polar ocean reached a record high of 20.87°C, 0.51°C above the 1991–2020 average.
Environmental Concerns
Increased levels of water vapor in the atmosphere, extreme temperatures, and high humidity contributed to elevated heat stress levels during 2024. The global area affected by at least ‘strong heat stress’ reached a new record annual maximum on 10 July, highlighting the urgency of addressing climate change impacts.
Carbon Dioxide and Methane Levels
Atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide and methane continued to rise in 2024, reaching record annual levels of 422 parts per million (ppm) and 1897 parts per billion (ppb) respectively. These trends underscore the ongoing challenge of reducing greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the effects of climate change.