International Shipping on Track to Achieve Zero Emissions by 2050
International shipping is set to make significant strides towards reducing its carbon footprint, with the goal of reaching zero or very near zero tank-to-wake (TTW) CO2 emissions by 2050. A recent report commissioned by the UK Department for Transport, conducted by ERM, UMAS, and UCL, highlights the potential for the maritime industry to achieve 95%+ reductions in well-to-wake (WTW) greenhouse gas emissions from 2018 levels, in alignment with a 1.5°C global temperature goal.
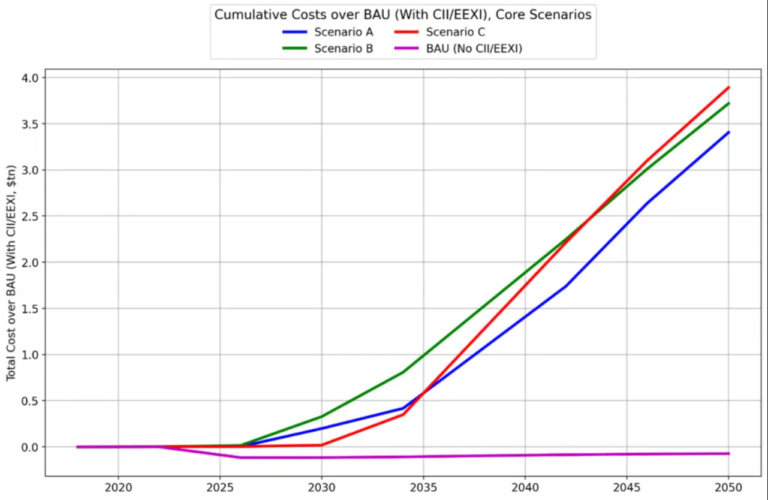
Core Scenarios for Decarbonization
The study utilized UMAS’ Global Maritime Transport Model to analyze three core scenarios for decarbonization. Scenario A involves gradual reductions in TTW CO2 emissions starting in 2025, Scenario C delays action until 2030 but then implements rapid cuts, and Scenario B aims for rapid reductions from 2025-2035 to achieve a 10% lower cumulative TTW CO2 emissions. In all scenarios, international shipping is projected to achieve zero or near-zero TTW CO2 emissions by 2050, alongside substantial reductions in WTW GHG emissions.
Cost Implications and Fuel Options
According to UMAS, the costs of decarbonization vary based on the timing of emission reductions. Each year of delay in initiating decarbonization efforts adds an estimated $100 billion to the total cost. The study emphasizes that early action is crucial to minimize disruptive technology changes and overall transition costs. The preferred pathway involves the widespread adoption of low-carbon ammonia, although alternatives like low-carbon methanol and hydrogen are also viable but at a higher cost.
Rapid Growth in Ammonia Demand
The core scenarios anticipate a rapid increase in demand for low-carbon ammonia, with the fuel becoming the primary choice for the shipping sector by the 2040s. To meet this demand, global ammonia production capacity would need to quadruple by the 2040s, necessitating urgent action to facilitate investment and policy frameworks that support the transition.
Policy Recommendations for Accelerated Decarbonization
UMAS underscores the importance of policies that consider well-to-wake (WTW) GHG emissions in addition to TTW CO2 emissions. Current policies that focus solely on TTW emissions may inadvertently incentivize solutions like Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG), which have significant upstream and non-CO2 GHG emissions. To expedite the adoption of vessel efficiency measures and low-carbon fuels, policy stringency must increase and align with WTW emissions considerations.